Chapter 6: Edge Security and Privacy: Difference between revisions
Ali Siddiqi (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Ali Siddiqi (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==='''DDoS'''=== | ==='''DDoS'''=== | ||
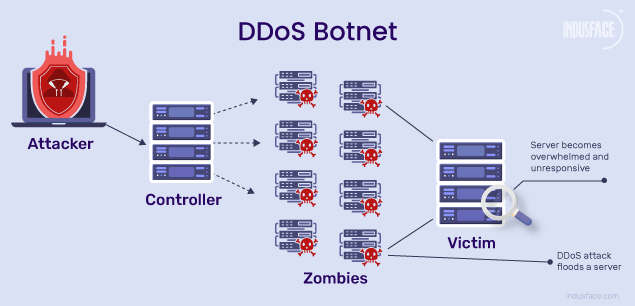
''DDoS'' is a type of cyberattack in which an attacker aims to disrupt services provided by one or more servers based on distributed based on distributed resources such as a cluster of compromised Edge devices, which are also known as ''botnets''. ''DDoS attacks'' occur when an attacker persistently sends streams of packets to a victim from compromised electronic devices, which causes the hardware resources of the victim to be quickly exhausted by handling these malicious packets and can no longer process any legitimate request on time. There are two kinds of DDoS attacks: Flooding-based and Zero-day DDoS attacks. | ''DDoS'' is a type of cyberattack in which an attacker aims to disrupt services provided by one or more servers based on distributed based on distributed resources such as a cluster of compromised Edge devices, which are also known as ''botnets''. ''DDoS attacks'' occur when an attacker persistently sends streams of packets to a victim from compromised electronic devices, which causes the hardware resources of the victim to be quickly exhausted by handling these malicious packets and can no longer process any legitimate request on time. There are two kinds of DDoS attacks: Flooding-based and Zero-day DDoS attacks. | ||
[[File: DDoS-Botnet.png]] | [[File: DDoS-Botnet.png]] | ||
Revision as of 02:12, 6 April 2025
6. Edge Security and Privacy
6.1 Overview of Security Challenges in Edge Computing
From previous chapters, Edge Computing has shown that it is here to stay and it will keep rapidly growing throughout the years. However, Edge Computing has its own security challenges that have to be addressed, because it is not a perfect system. Edge Computing has many security challenges that have to be dealt with in order to keep data safe.
DDoS
DDoS is a type of cyberattack in which an attacker aims to disrupt services provided by one or more servers based on distributed based on distributed resources such as a cluster of compromised Edge devices, which are also known as botnets. DDoS attacks occur when an attacker persistently sends streams of packets to a victim from compromised electronic devices, which causes the hardware resources of the victim to be quickly exhausted by handling these malicious packets and can no longer process any legitimate request on time. There are two kinds of DDoS attacks: Flooding-based and Zero-day DDoS attacks.