Introduction to Edge Computing
Introduction to Edge Computing
Edge computing was developed to address the challenges of cloud computing, such as slow response times, security risks, and the overwhelming data traffic caused by the increasing number of internet-connected smart devices. By processing data closer to its source instead of relying on distant cloud servers, edge computing ensures faster and more efficient performance.
With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the early 2000s, experts predicted that by 2019, a significant share of IoT data would be processed at the edge rather than in centralized cloud data centers. This shift was driven by the need for rapid responses in applications like self-driving cars and smart cities, where even minor delays could have serious consequences. Unlike traditional cloud computing, edge computing enhances security, reduces latency, and processes data locally, relieving pressure on the internet while improving overall efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, edge computing plays a crucial role in enabling faster, safer, and more reliable digital experiences.
1.1 What is Edge Computing?
1.2 Why we need Edge Computing?
1.3 Edge Computing application Domains and Typical Applications
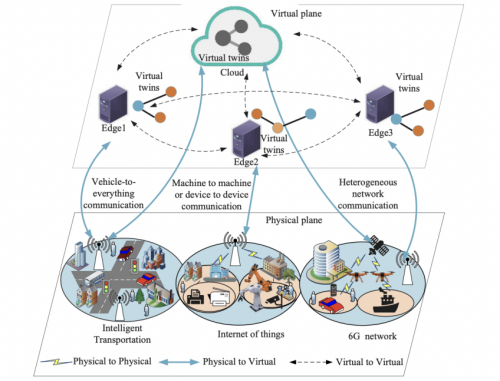
Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency, bandwidth usage, and reliance on cloud computing. This approach is transforming various industries by enabling real-time analytics, automation, and enhanced decision-making. Below is a detailed explanation of each domain and how edge computing is applied within them.
1.3.2 Autonomous Vehicles & Transportation
The transportation sector requires real-time data processing for safety, efficiency, and automation. Autonomous vehicles, smart traffic systems, and connected infrastructure rely on low-latency computing to function effectively.
1.3.2 Industrial IoT (IIoT) & Manufacturing
Factories and industrial plants increasingly integrate IoT devices for automation, quality control, and predictive maintenance. These operations require real-time decision-making to minimize downtime and optimize efficiency.
1.3.3 Energy & Smart Grids
The energy sector is undergoing a digital transformation, integrating smart grids, renewable energy sources, and real-time energy management solutions. These systems must process large volumes of data efficiently.
1.3.4 Smart Cities & Infrastructure
Smart cities integrate edge computing for efficient urban management, security, and environmental monitoring. Data is processed locally to reduce network congestion and response times.
1.3.5 Telecommunications & 5G Networks
Telecommunications providers leverage edge computing to improve network performance, reduce latency, and optimize bandwidth usage. 5G networks particularly benefit from distributed processing at the edge.
1.3.6 Healthcare
Healthcare systems generate massive amounts of data from medical devices, imaging systems, and patient monitoring. Real-time processing is critical for quick diagnosis, treatment, and remote patient care.
1.4 Different Edge Computing Paradigms
References
- “ Edge Computing: Vision and Challenges” - IEEE Internet of Things Journal
- "An Overview on Edge Computing Research"
- "A Survey on Edge Computing for the Internet of Things" – ACM Computing Surveys.