Edge Cloud: Bringing Computing Close to the User
Author: Prateek Rai Srivastav
What is Edge Cloud?
Edge Cloud is a distributed computing paradigm that extends cloud capabilities closer to end users and devices. Instead of relying solely on centralized data centers, edge cloud leverages geographically distributed nodes to process data at the edge of the network, reducing latency and improving performance for real-time applications.
Key Benefits of Edge Cloud
Low Latency & Faster response times
By processing data closer to users, edge cloud reduces the delay in applications like autonomous vehicles, IoT, and AR/VR. For example, a smart city traffic system can analyze video feeds locally instead of sending everything to a distant cloud
Bandwidth optimization & Cost reduction
- Since data is processed near the source, less raw data needs to be sent to the cloud, reducing bandwidth usage.
- This is crucial for IoT devices, which generate massive amounts of data.
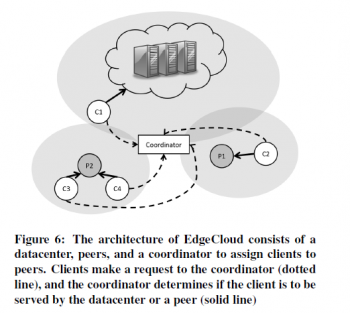
Use Cases of Edge Cloud
- Smart Cities & IoT : Traffic monitoring, smart grids, and public safety rely on edge cloud for real-time decision-making without relying on remote data centers.
Example: AI-powered traffic cameras process video on-site to detect congestion and adjust traffic lights dynamically.
- AI & Machine Learning at the Edge : Edge cloud enables AI inference directly on devices like surveillance cameras, drones, and robots.
Example: A facial recognition system on a retail store’s edge server can process images locally instead of sending them to a central cloud, ensuring faster results and better privacy.